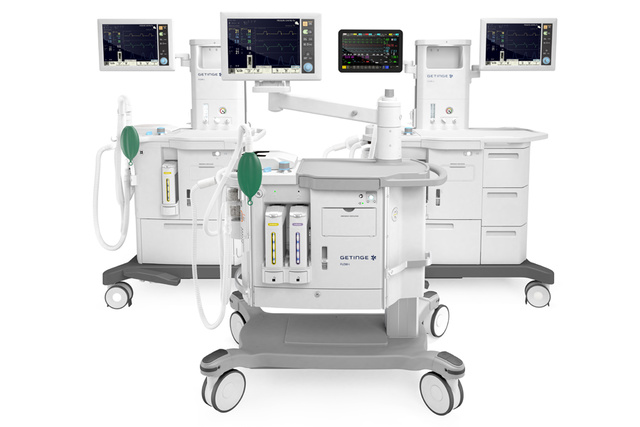
Dynamic Anesthesia Delivery
When Every Breath. Counts. ゲティンゲの麻酔テクノロジー
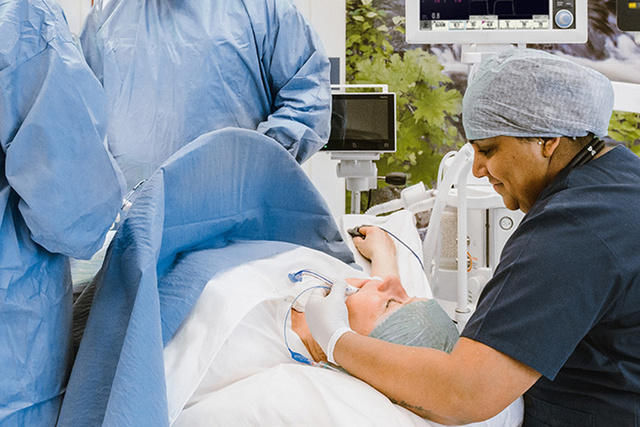
ゲティンゲ独自の麻酔テクノロジーが違いを生みます
ゲティンゲは、患者の安全とケアの効率化に注力しています。そして Flow Family 麻酔システム用に Dynamic Anesthesia Delivery 技術を開発しました。これは、臨床医の制御の下で、あらゆる患者、症例、状況に応じた安全で正確な麻酔を提供する先進的な技術です。
自動ガスコントロールで 58 % 削減
患者の安全性を損なうことのない、持続可能で経済的なアプローチ。
Flow Family 麻酔システムにおけるゲティンゲ独自の麻酔イノベーション「自動ガスコントロール(AGC)」は、セボフルランの消費量を最大 58 % 削減します。[3]