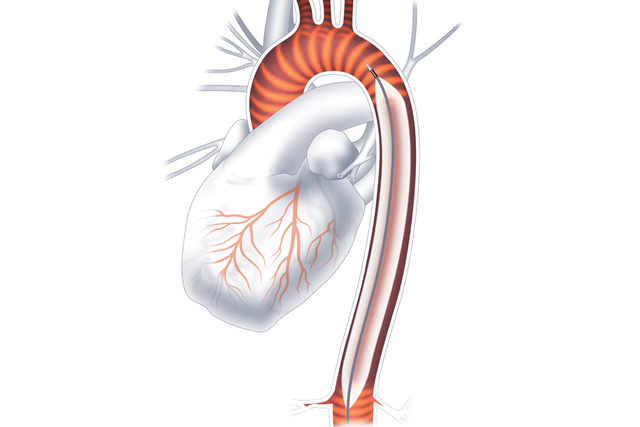
Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Therapy
The predominant MCS device -
a trusted, valuable first-line option

IABP Therapy: 50+ Years of Heart Support
The intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) was the first and is still the most used mechanical circulatory support device.[1] Straightforward insertion, ready availability and low cost have made IAPB use common in the treatment of the acute heart failure. When positioned in a timely manner, it can play a critical role in the rescue of patients with acute ischemic MI.[2]
If you are a current user of our IAB and IABP devices, please click on the link below to find the latest product support and software update information.
The Science Behind IABP Therapy
This on-demand webinar will enhance your knowledge of the physiological and clinical effects as well as the therapeutic rationale for intra-aortic balloon pump therapy.
MCS device selection in HF patients - Where does counterpulsation fit?
This video session focuses on the unique physiological effects of counterpulsation in advanced heart failure patients. Moreover, the session provides guidance on MCS selection based on underlying etiology, clinical phenotyping, and predictors for positive hemodynamic and clinical response. Finally, you will be presented with novel applications for counterpulsation in HF.

SCAI SHOCK Stage Classification Expert Consensus Update: A Review and Incorporation of Validation Studies
Since 2019, the SCAI SHOCK stage classification has been widely adopted and subsequently validated by multiple groups across the spectrum of CS. The SCAI SHOCK consensus workgroup reviewed the validation studies in detail to identify potential areas of refinement for the classification scheme.
Influence of intra-aortic balloon pump on mortality as a function of cardiogenic shock severity
IABP use was associated with substantially lower in-hospital mortality in patients with CS, without differences in this effect across the SCAI shock stages.

Fiber-Optic Balloons
Faster set-up compared to conventional IABs with no need to level and zero the arterial line, simplified pressure monitoring with in vivo calibration.[3]
Trial |
IABP |
No IABP |
P value |
| BCIS-1[7] major bleeding | 3.3% | 4.0% | 0.77 |
| CRISP AMI[8] major bleeding | 3.1% | 1.7% | 0.49 |
| CRISP AMI[9] major vascular | 4.3% | 1.1% | 0.09 |
| IABP-SHOCK II[9] moderate bleeding | 17.3% | 16.4% | 0.77 |
| IABP-SHOCK II[9] major bleeding | 3.3% | 4.4% | 0.51 |
| IABP-SHOCK II[9] major vascular | 4.3% | 3.4% | 0.53 |
Explore our products
Find the right products and solutions for you