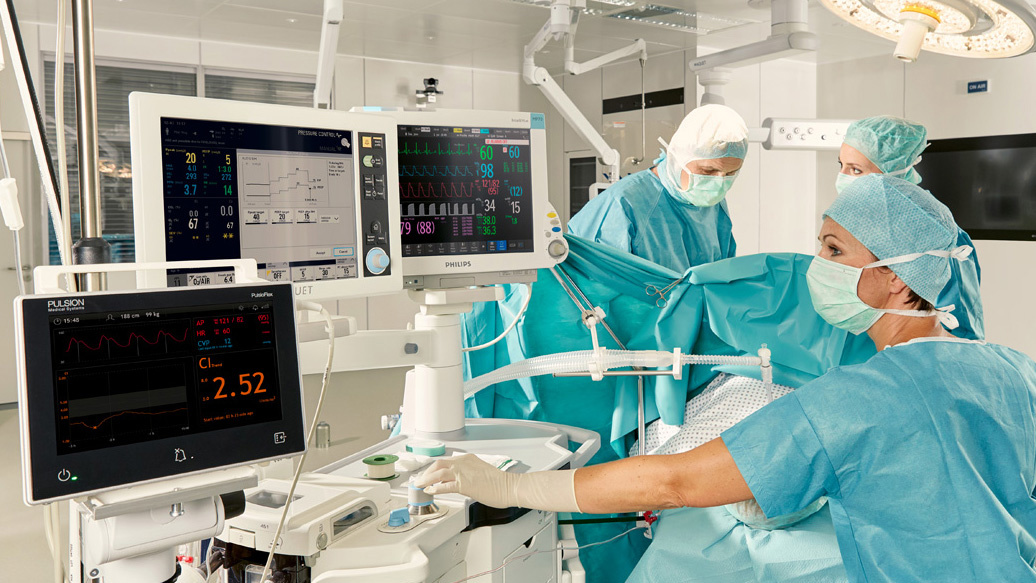
Combine mechanical ventilation and advanced monitoring
The physiological increase of intrathoracic pressures - when performing mechanical ventilation during surgeries - has hemodynamic consequences. The anesthesiologist can monitor shifts in cardiac index, and the blood flow proactively by using minimally invasive hemodynamic monitoring prior, during, and after complex surgical interventions.
Hand in hand for better patient care
- Before the stepwise recruitment maneuver (RM) it’s advisable to optimize the patient’s volume status
- During the RM shifts in the cardiac output should be monitored closely
- After the RM patients with noticeable stroke volume variation are likely to be preload responsive and cardiac output may increase with fluids
Thus, monitoring the hemodynamic condition during ventilation phases and initiating proactive therapy decisions, allows the safe implementation of lung-protective ventilation strategies.
A good ventilatory strategy involves a good hemodynamic strategy.
Did you know that atelectasis affects over 90 % patients undergoing surgery? [1]
Anesthesia-induced lung collapse is a well-known entity which can be avoided by a good ventilatory strategy. Flow-i’s new lung recruitment maneuver aims to gently open the alveoli to make a lasting difference for your patients.
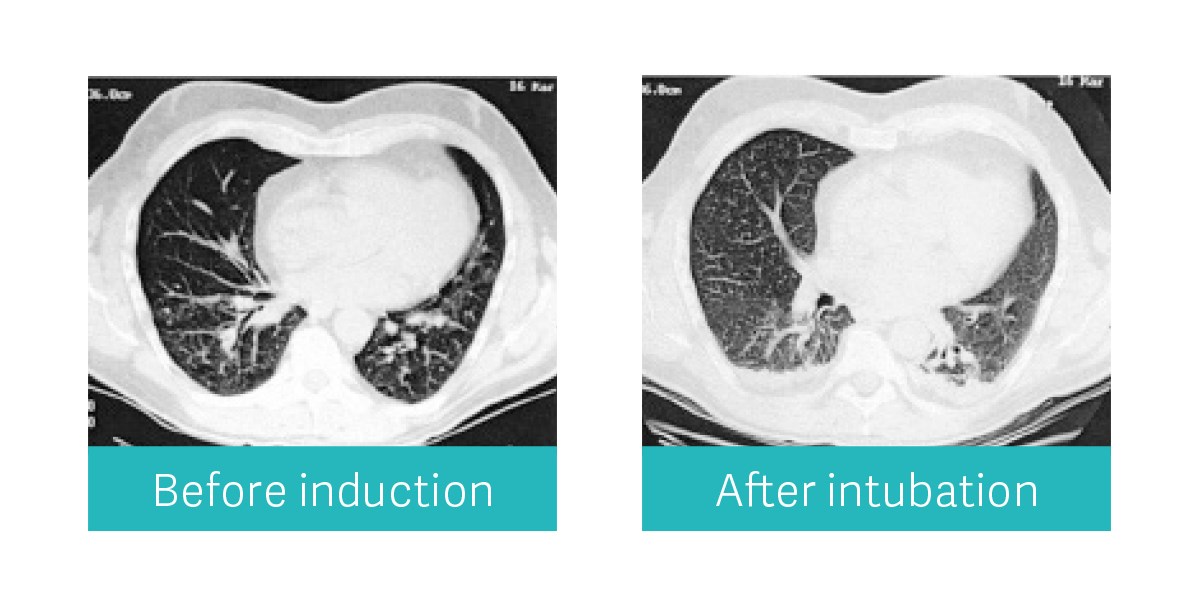
Postoperative pulmonary complications
- Hypoxemia
- Pneumonia
- Local inflammatory response
- Ventilator induced lung injury
In the automatic recruitment maneuver, a stepwise increase in pressure is applied for a time period set by the user. It’s designed to reduce the occurrence of hemodynamic compromise. In combination with the ProAQT technology it is possible to detect any hemodynamic changes automatically, continuously and in real time – prior, during and after an recruitment maneuver.
Lung protective ventilation helps
In a stepwise recruitment maneuver there will be less hemodynamic compromise.
Lung recruitment with Maquet Flow-i allows you to choose between an automatic or manual maneuver. Whichever you choose, the recruitment will be stepwise. Flow-i measures and displays the dynamic compliance in real time, which is used to find the optimal lowest PEEP that keeps the lungs open.
Advanced hemodynamic monitoring helps
Use of Advanced Patient Monitoring shows the response of your patient to lung recruitment.
The change of CO and SV is detected in realtime. Also Preload (SVV, PPV), Afterload (SVRI) and Contractility (dPmx, CPI) parameters provide clinicians better insights.
Occult hypovolemia can be detected prior to the recruitment maneuver followed by appropriate perioperative fluid management that will decrease post-surgical complications.
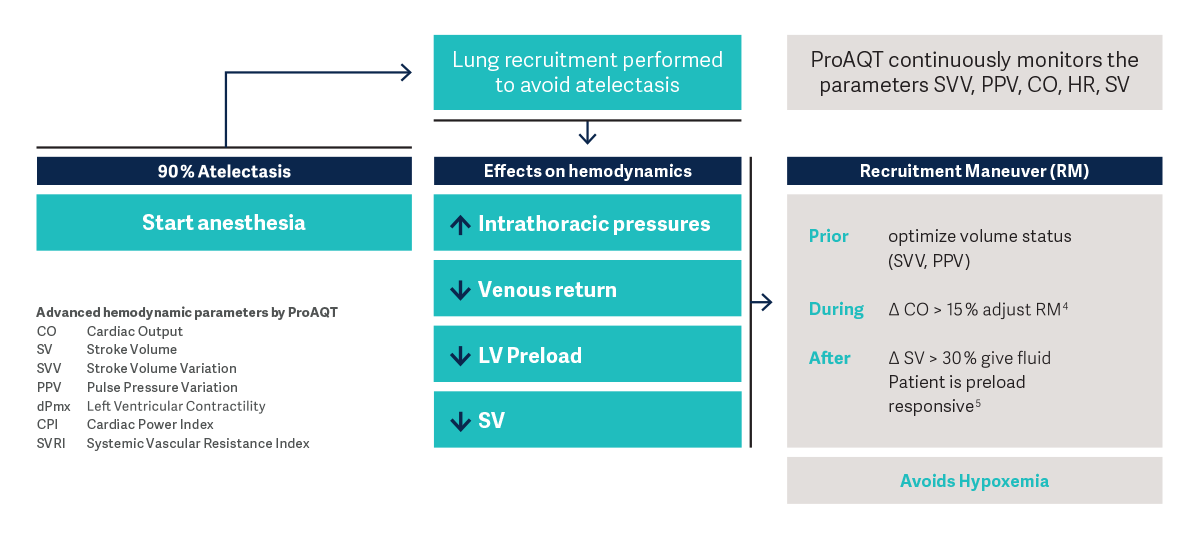
Heart-lung interactions during the recruitment maneuver can be monitored by the ProAQT technology
Visualize hemodynamic conditions
Fluid management fact
37 % – 55 %
of postoperative complications can
be prevented through perioperative
goal directed fluid therapy.[2], [3]
Safety and simplicity for lung recruitment in the OR
Lung recruitment fact
5 – 10 %
of all surgical patients develop Postoperative
Pulmonary Complications (PPCs).
In thoracic or abdominal surgeries
even up to 30 – 40 % develop PPCs .[4]
Read the full case report
Intraoperative ventilatory management in an obese patient